Chorionic Villus Sampling, What Is It And Does it Effect You?
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a test which is performed to identify a number of different genetic problems – including Down syndrome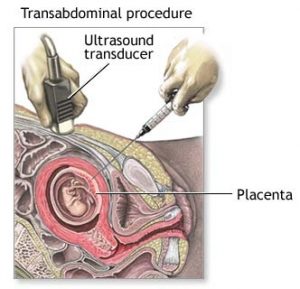 This test is performed by using a tin tube which is guided through your cervix or by using a thing needle which is inserted into your uterus. Your health care provider will then take a sample of chorionic villi from the placenta. The Chronic villi have the same genetic makeup as your baby and are responsible for transferring nutrients, oxygen and antibodies from you to your baby.
This test is usually performed at the end of the first trimester between the 9th and 14th week of your pregnancy.
This test is performed by using a tin tube which is guided through your cervix or by using a thing needle which is inserted into your uterus. Your health care provider will then take a sample of chorionic villi from the placenta. The Chronic villi have the same genetic makeup as your baby and are responsible for transferring nutrients, oxygen and antibodies from you to your baby.
This test is usually performed at the end of the first trimester between the 9th and 14th week of your pregnancy.
Who might need chorionic villus sampling?
Since Chorionic villus sampling has the ability to detect and genetic problem earlier in your pregnancy than any other test, this test may be offered to anyone who may be at risk of delivering a baby which may have chromosomal or genetic disorders. It may also be offered to you if one of your earlier screening tests has returned results which are cause for concern.What Complications Will CSV Detect?
Like amniocentesis – CVS can identify:- Nearly all chromosomal abnormalities, including Down syndrome, trisomy 13, trisomy 18, and sex chromosome abnormalities (such as Turner syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome). CSV is more than 99 percent accurate in diagnosing these conditions
- Several hundred genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and Tay-Sachs disease. The test is not used to look for all of them, but if your baby is at increased risk for one or more of these disorders, CVS can usually tell you whether he has the disease
- Unlike amniocentesis, CVS cannot detect neural tube defects, such as spina bifida. If you opt for CVS, you’ll be offered a blood screening test in your second trimester to determine whether you’re at increased risk for neural tube defects. Most neural tube defects can be detected by a detailed second-trimester ultrasound
- Be aware that if you have CVS, there’s a 1 percent chance of getting a result called a mosaicism, in which some of the cell lines cultured from the placenta contain abnormal chromosomes and some are normal. If your CVS detects a mosaicism, then you will have to have amniocentesis and possibly other testing to determine whether your baby is affected or not
How accurate are the results?
Chorionic villus sampling, he chance of a false-positive is less than 1 percentWhat are the risks associate with Chorionic villus sampling
- Miscarriage. Chorionic villus sampling has a 1% risk of miscarriage.
- Cramping and vaginal bleeding. Experiencing some cramping and bleeding post CSV is common – especially if the sample was taken through the cervix. If this develops into heavy bleeding or a fever after CSV, contact your health care provider
- Rh sensitization. Chorionic villus sampling may cause some of the baby’s blood cells to enter your bloodstream. If you have Rh-negative blood and your baby has Rh-positive blood, you’ll be given a drug called Rh immunoglobulin after the test to prevent you from producing antibodies against your baby’s blood cells
What happens after chorionic villus sampling?
Most CSV tests return normal results, and if this is the case then in most occasions a follow-up ultrasound is recommended a few days post testing just to confirm your babies health. If the test does return results showing a genetic disorder that can’t be treated, then you will and your partner will need to discuss your options which are available to you.Chorionic Villus Sampling



