Amniocentesis Pregnancy Test
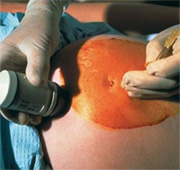 During an amniocentesis test a small sample of amniotic fluid which surrounds the fetus is removed and examined, usually to diagnose or rule out the possibility of birth defects and other complications. An amniocentesis is usually carried out around 15-18 weeks.
Amniocentesis is the most common prenatal test used to diagnose chromosomal and genetic birth defects which lead to Down Syndrome. There is another test which is also used known as chorionic villus sampling (CVS), which can also be used to diagnose most, but not all, of the same birth defects as an amniocentesis.
This test is usually carried out earlier than an amniocentesis, around 10-15 weeks. There are downsides to CVS, and possibly the main being a high risk of miscarriage.
During an amniocentesis test a small sample of amniotic fluid which surrounds the fetus is removed and examined, usually to diagnose or rule out the possibility of birth defects and other complications. An amniocentesis is usually carried out around 15-18 weeks.
Amniocentesis is the most common prenatal test used to diagnose chromosomal and genetic birth defects which lead to Down Syndrome. There is another test which is also used known as chorionic villus sampling (CVS), which can also be used to diagnose most, but not all, of the same birth defects as an amniocentesis.
This test is usually carried out earlier than an amniocentesis, around 10-15 weeks. There are downsides to CVS, and possibly the main being a high risk of miscarriage.
Who will need an amniocentesis test?
Amniocentesis is not offered to all women who are pregnant because it does carry a small risk of miscarriage and so it is generally offered to pregnant women who may be showing signs that their baby may have some chromosomal or genetic birth defects, or to those who may be at a higher risk of these sorts of complications.Reasons for needing an amniocentesis test
- Maternal age. If you are going to be 35 or older at the time of delivery, your healthcare provider may offer you an amniocentesis test. There is a higher risk of Down Syndrome and chromosomal disorders in women who are pregnant over 35.
- A previous child or pregnancy with a birth defect. Your healthcare provider will certainly offer this test to you if you have previously had a child which may have been born with birth defects or chromosomal disorders. If other members in your family have had a history of birth defects then you may also be offered this test.
- Suggestive screening test results. You may be offered to have an amniocentesis done if other tests are showing indications that there may be chromosomal disorders.
How is amniocentesis performed?
Amniocentesis is performed by inserting a thin, hollow needle into the uterus and removing some of the amniotic fluid that surrounds the baby. This is usually carried out by having the pregnant woman lie flat on her back on a table. Her belly is cleansed with an iodine solution. The healthcare provider would then use an ultrasound to help guide the doctor as the needle is inserted through the abdomen into the uterus and into the amniotic sac. About 2 tablespoons (30ml) of amniotic fluid is then removed. This usually only takes a few minutes to complete. Once the fluid has been withdrawn your healthcare provider will then use the ultrasound to monitor your baby’s heartbeat for a few minutes to ensure that the fetal heartbeat is normal and the baby is not under any distress. It is not a painful procedure, although about 2% of women do report experiencing some cramping when the needle enters the uterus. Some women also report some spotting and amniotic fluid leaking after having had the amniocentesis. Your health care provider will probably recommend that you avoid any physical activity for a few hours after the procedure is complete. Once the fluid is removed it is sent to a lab for analysis. Test results are usually available within 3 weeks.Is amniocentesis safe?
Amniocentesis does have a slight risk of miscarriage, however the rate of miscarriage is 1 in 400. It also leaves a chance of uterine infection, but the chances of this are even less than a miscarriage, with the chances of 1 in 1000. Pregnancy VideoRelated Video In our pregnancy video section we have a whole range of videos for you to watch which cover a whole range of subjects, from general pregnancy, complications, newborn care and even beauty.
Pregnancy VideoRelated Video In our pregnancy video section we have a whole range of videos for you to watch which cover a whole range of subjects, from general pregnancy, complications, newborn care and even beauty.Amniocentesis