Chicken Pox During Pregnancy
 It is not uncommon that pregnant women come into contact with someone who has the chicken pox virus and this can be a great concern to them. Almost 90% of women who come into contact with the chicken pox virus are safe – this could either be because they have had chicken pox before, or because they have had immunizations as a young child.
It is not uncommon that pregnant women come into contact with someone who has the chicken pox virus and this can be a great concern to them. Almost 90% of women who come into contact with the chicken pox virus are safe – this could either be because they have had chicken pox before, or because they have had immunizations as a young child.
What can happen to my baby if I get chicken pox?
In most cases if you get chicken pox during the course of your pregnancy your baby will be fine. What determines if they will be affected or not is the time frame in which you get chicken pox. Should you contract the virus during the early stages of your pregnancy then there is a risk that your baby may develop varicella syndrome. This condition may lead to the possibility of the following conditions developing in your baby:- Poor growth in utero
- Birth defects
- Skin scarring
- Malformed limbs
- Abnormally small head
- Vision or hearing problems
- Motor or mental developmental disabilities
Symptoms of chicken pox?
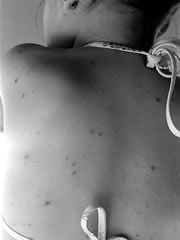
Chicken pox is highly infectious and can be passed on by droplets through the air and via contact. The infection causes fever, a feeling of generally being unwell and an itchy rash which develops into small vesicles which crust over before healing. The average incubation period for chicken pox is two weeks. What this means is that the early signs that you may have chicken pox may only show themselves 2 weeks from when you come into contact wiht the virus.Treating chicken pox
Should you become in contact with someone who has chicken pox you should alert your healthcare provider. In most cases you may be given a dose of man made antibodies know as Varicella-Zoster Ig of which this must be administered no more than 10 days after you have come in contact with the virus.Chickenpox